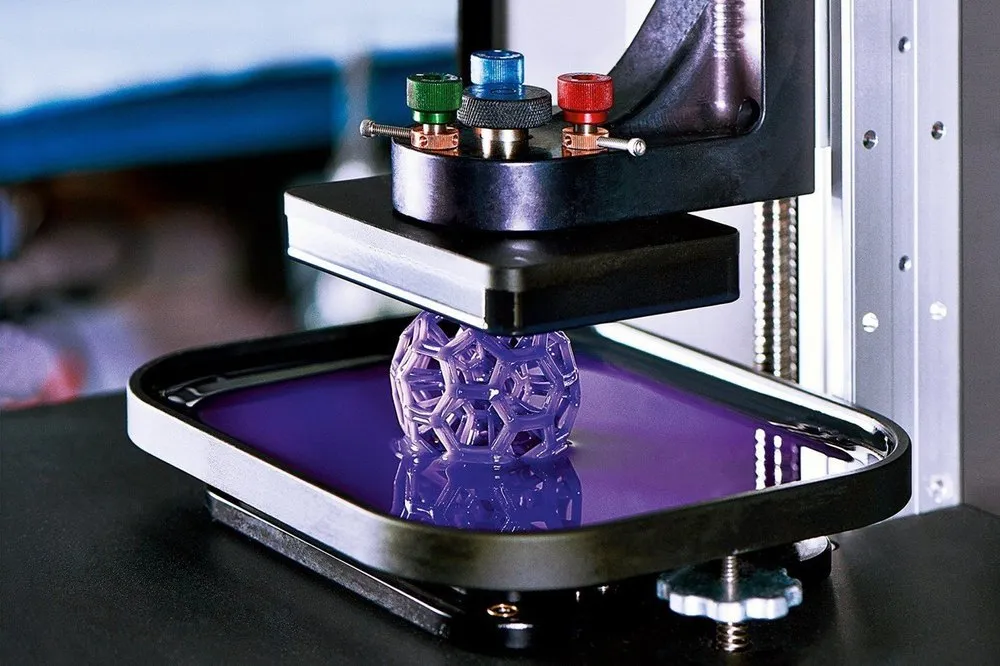
In the fast-paced world of technology, 3D printing has emerged as a revolutionary force, transforming industries ranging from healthcare to automotive manufacturing. 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, allows for the creation of complex, customized objects layer by layer, using digital designs. In this blog, we will explore the cutting-edge 3D printing technologies, their applications, and how they are reshaping industries worldwide.

History of 3D Printing:
The first 3D printer formed in 1981, when Dr. Hideo Kodama invented one of the first rapid prototyping machines that created parts bracket by bracket, applying a resin that could be polymerized by UV light. In 1986, the original patent for stereolithography (SLA) was filed by Chuck Hull, who’s called “the innovator of 3D printing” for creating and commercializing both SLA and the. stl format – the most common file type used for 3D printing.
In 1988, Carl Deckard, a scholar at the University of Texas, authorized selective laser sintering (SLS) technology – another type of 3D printing that uses a laser to sinter powdered material into solid structures. Shortly later, in 1989, Scott Crump patented fused deposit modelling (FDM) – also known as fused hair fabrication (FFF) – and innovated Stratasys, one of the main players in the 3D printing industry to this day. That same time, Hull’s company, 3D Systems Corporation, released the SLA- 1 3D printer.

Dr. Hideo Kodama

Chuck Hull

Carl Deckard

Scott Crump
1. What is 3D Printing Technology?
3D printing technology refers to the process of creating three-dimensional objects using computer-aided design (CAD) files. Unlike traditional manufacturing methods, 3D printing builds objects layer by layer, making it possible to create intricate designs with precision and reduced waste.
Key advantages of 3D printing include:
- Customization and personalization
- Rapid prototyping
- Reduced material waste
- Cost-effective small-batch production
2. Types of 3D Printing Technologies
Several 3D printing technologies cater to diverse industry needs. Let’s look at the most prominent ones:
a. Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
- Process: FDM uses a thermoplastic filament that is heated and extruded through a nozzle to build layers.
- Applications: Prototypes, low-cost manufacturing, and household products.
- Industries: Consumer goods, education, and small-scale production.
b. Stereolithography (SLA)
- Process: SLA uses a UV laser to cure liquid resin layer by layer, creating smooth and precise parts.
- Applications: Dental models, jewelry, and detailed prototypes.
- Industries: Healthcare, aerospace, and automotive.
c. Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
- Process: SLS uses a laser to fuse powdered materials (like nylon) into solid objects.
- Applications: Functional prototypes, end-use parts, and complex geometries.
- Industries: Engineering, automotive, and medical.
d. Digital Light Processing (DLP)
- Process: Similar to SLA, DLP uses a digital light projector to cure resin but at faster speeds.
- Applications: Dental appliances, prototypes, and artistic models.
- Industries: Healthcare, manufacturing, and arts.
e. Binder Jetting
- Process: Binder jetting uses a liquid binding agent to bond powdered materials, layer by layer.
- Applications: Sand casting molds, full-color prototypes, and low-cost metal parts.
- Industries: Foundry, architecture, and aerospace.
f. Metal 3D Printing (DMLS/SLM)
- Process: Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) and Selective Laser Melting (SLM) use lasers to fuse metal powder into solid parts.
- Applications: Complex metal components, tools, and prototypes.
- Industries: Aerospace, automotive, and medical implants.
3. Applications of 3D Printing Technologies
a. Healthcare Industry
3D printing has revolutionized medicine by enabling the creation of prosthetics, dental implants, and anatomical models. Bioprinting is another emerging field, allowing for the development of tissues and organs for transplantation.
b. Aerospace and Automotive
Industries like aerospace and automotive use 3D printing for lightweight, durable components. This technology reduces production time and costs while improving design flexibility.
c. Manufacturing and Prototyping
3D printing enables rapid prototyping, allowing manufacturers to test and iterate designs quickly. This accelerates product development cycles and reduces overall costs.
d. Consumer Goods and Fashion
From customized shoes to jewelry and home decor, 3D printing empowers designers to create personalized and unique products.
e. Education
In education, 3D printing enhances learning by enabling students to create physical models of complex concepts, making subjects like science and engineering more engaging.
4. Advantages of 3D Printing
- Cost-Effective: Reduces material waste and costs for small-batch production.
- Customization: Enables highly personalized products tailored to individual needs.
- Rapid Prototyping: Accelerates the design and testing process.
- Sustainability: Minimizes waste by using additive processes rather than subtractive.
- Design Flexibility: Allows for the creation of intricate, lightweight, and complex designs.
- Future of 3D Printing
The future of 3D printing is exciting and filled with possibilities. Key trends include:
Bioprinting
Advancements in creating human tissues and organs for medical use.

Construction
A construction method that uses 3D printers to build structures layer by layer.
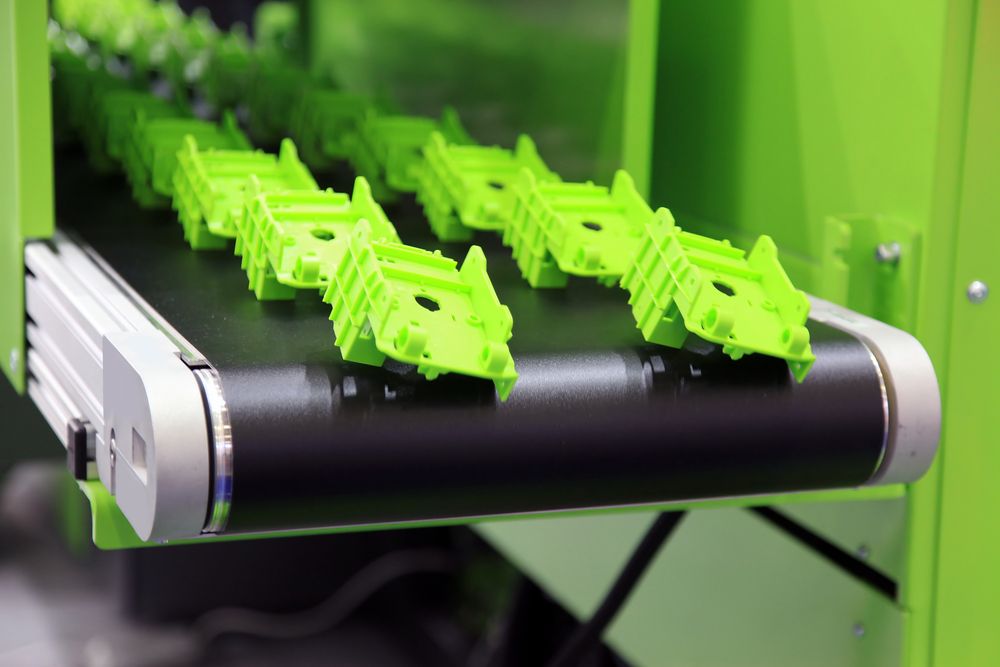

Mass Production
Scaling up 3D printing for large-scale manufacturing.

Space Exploration
Using 3D printing to create tools, habitats, and spare parts in space missions.
Conclusion
3D printing technologies are reshaping the manufacturing landscape, providing unprecedented opportunities for innovation, customization, and efficiency. From healthcare to aerospace, industries are leveraging this transformative technology to achieve faster, more cost-effective production processes. As advancements continue, 3D printing is set to become an even more integral part of our lives, paving the way for a smarter and more sustainable future.
Explore the future of manufacturing with 3D printing. Whether you’re looking for prototypes, functional components, or unique designs, 3D printing is the key to turning imagination into reality!
