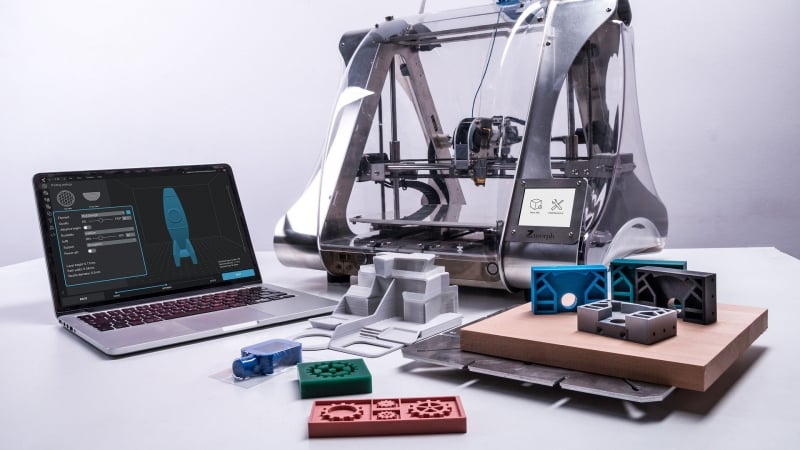
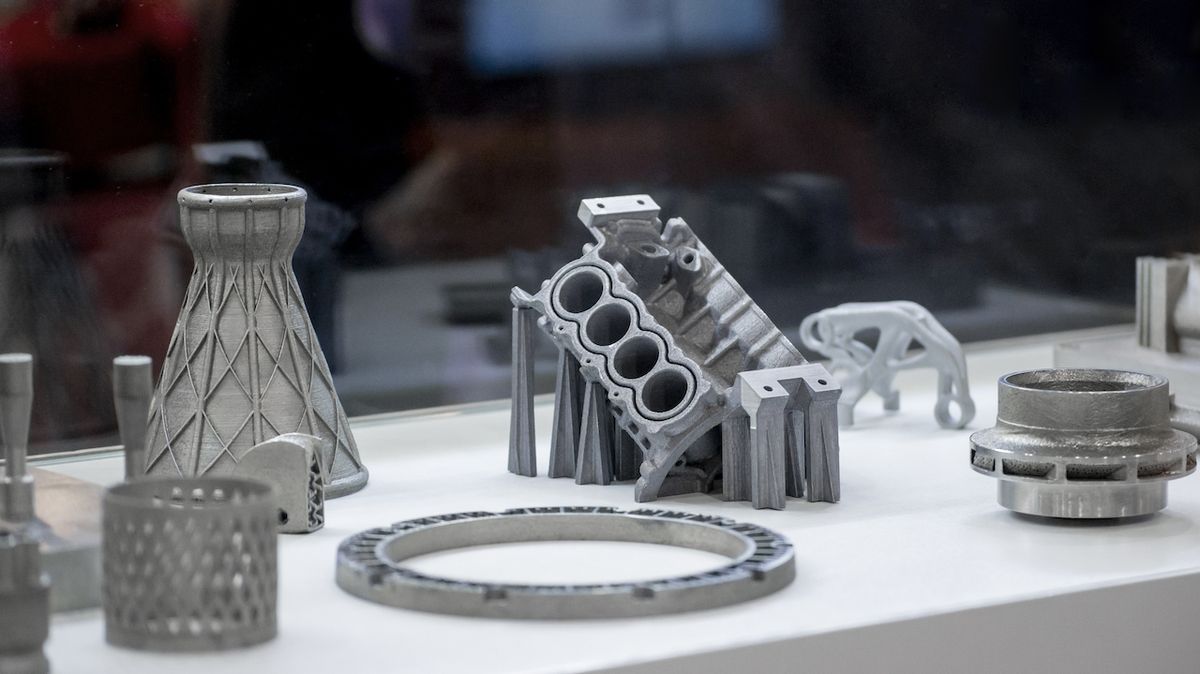
Industrial design is at the heart of product development, blending creativity, functionality, and manufacturability to bring ideas to life. With advancements in technology, 3D printing has emerged as a revolutionary tool that is reshaping how industrial designers approach their craft. Here, we explore how 3D printing enhances industrial design practices and its transformative impact on the industry.
1. Accelerated Prototyping
One of the most significant benefits of 3D printing is its ability to rapidly produce prototypes. Designers can create detailed and functional prototypes within hours, compared to traditional methods that take days or weeks. This speed allows for:
- Faster iteration cycles
- Immediate testing of form, fit, and functionality
- Early detection and rectification of design flaws
For example, a designer creating a new ergonomic tool handle can 3D print multiple iterations in a single day, testing each version for usability and comfort.
2. Enhanced Design Flexibility
3D printing removes many of the constraints imposed by traditional manufacturing methods. Complex geometries, intricate patterns, and customized designs that were once impossible or prohibitively expensive are now feasible. This freedom allows designers to:
- Explore unconventional aesthetics
- Optimize designs for specific functions
- Cater to niche markets with bespoke solutions
An industrial designer working on lightweight automotive components can use 3D printing to incorporate lattice structures that reduce weight while maintaining strength.
3. Cost Efficiency in Development
Traditional prototyping and tooling processes are expensive and time-consuming. 3D printing eliminates the need for costly molds and specialized machinery, making it a cost-effective option for:
- Small batch production
- Initial concept testing
- Customizable parts
By leveraging 3D printing, startups and small businesses can compete with larger companies by reducing upfront development costs.
4. Material Versatility
3D printing technologies support a wide range of materials, including plastics, metals, resins, and composites. This versatility enables designers to:
- Experiment with different material properties
- Create multi-material prototypes
- Develop parts with specific mechanical, thermal, or chemical characteristics
For instance, industrial designers in the healthcare sector can create prototypes of medical devices using biocompatible materials.
5. Improved Collaboration
3D printing enhances collaboration between designers, engineers, and stakeholders. Physical prototypes provide a tangible way to:
- Communicate ideas effectively
- Gather feedback from clients and team members
- Facilitate decision-making processes
A physical model of a product design can bridge the gap between technical drawings and client expectations, ensuring alignment before moving to production.
6. Sustainability and Waste Reduction
Additive manufacturing processes like 3D printing generate minimal waste compared to subtractive methods. Designers can:
- Produce only the material needed
- Optimize designs for material efficiency
- Contribute to sustainable manufacturing practices
This makes 3D printing an environmentally friendly option for industrial design projects, aligning with global efforts to reduce waste.
7. Bridging the Gap Between Concept and Production
3D printing enables a seamless transition from concept to production by providing realistic and functional prototypes. It allows designers to:
- Validate designs under real-world conditions
- Perform stress testing on functional prototypes
- Streamline the handoff to manufacturing teams
For example, a consumer electronics company can 3D print functional prototypes of a new gadget to test its usability and durability before committing to mass production.
Conclusion
3D printing is revolutionizing industrial design practices by empowering designers with unprecedented speed, flexibility, and efficiency. Its ability to produce complex, cost-effective, and sustainable designs ensures that it will continue to play a critical role in shaping the future of industrial design. As technology advances, industrial designers who embrace 3D printing will find themselves at the forefront of innovation, delivering better products faster and more sustainably than ever before.
Services we offer at Kreate 3D in Pune, Mumbai, Nashik, Aurangabad, Nagpur, Kolhapur, Goa, Belagavi
FDM 3D Printing Services, SLA 3D Printing Services, SLS 3D Printing Services, MJF 3D Printing Services, Metal 3D Printing Services, Vacuum Casting Services , 3D Scanning Services, Reverse Engineering Services & All Type Of Prototyping Services. Zortrax FDM 3D Printer (M300 Dual,M300 Plus, M200 Plus), Formlabs SLA 3D Printer (Form 4, Form 4L,Form 4B, Form 4BL), Thor 3D Scanner (Calibry, Calibry Mini).